Drug-prompted photosensitivity refers to the development of cutaneous disease as a result of the mixed effects of a chemical and light. publicity to both the chemical or the sunshine alone isn't adequate to induce the disease; on the other hand, when photoactivation of the chemical occurs, one or more cutaneous manifestations may come up. These embody phototoxic and photoallergic reactions, a planus lichenoides response, pseudoporphyria, and subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Photosensitivity reactions may just consequence from systemic drugs and topically applied compounds (see desk 1 beneath).
Wavelengths within the UV-A (320-four hundred nm) vary and, for certain compounds, within the visible vary, are more likely to lead to drug-brought about photosensitivity reactions, although every now and then UV-B (290-320 nm) may also be responsible for such effects. UV-B wavelengths are most efficient at inflicting sunburn and nonmelanoma skin cancer. In sufferers who present with photosensitivity, it's ceaselessly troublesome to distinguish phototoxic from photoallergic reactions. however, they have got quite a few distinguishing characteristics (see table 2 below).
table 1. in style Photosensitizing drugs (Open table in a brand new window)
class medication photograph-poisonous response picture-hypersensitive reaction Lichenoid reaction Pseudo-porphyria Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus AntibioticsTetracyclines (doxycycline, tetracycline)YesNoYesYesNoFluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, levofloxacin)[1] YesNoNoNoNoSulfonamidesYesNoNoNoNoNonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[2] IbuprofenYesNoYesNoNoKetoprofenYesYesNoNoNoNaproxen[3] YesNoYesYesNoCelecoxib[4] NoYesNoYesNoDiureticsFurosemideYesNoNoYesNoBumetanideNoNoNoYesNoHydro-chlorothiazideYesNoNoNoYesRetinoidIsotretinoinYesNoNoNoNoAcitretinYesNoNoNoNoHypoglycemicsSulfonylureas (glipizide, glyburide)[1] NoYesYesYesNoHMG-CoA* reductase inhibitorsStatins (atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin)[5] YesYesYesYesNoEpidermal growth issue receptor inhibitorsCetuximab, panitumumab, erlotinib, gefitinib, lapatinib, vandetanib[6] YesYesYesYesNoPhotodynamic remedy prophoto-sensitizers5-Aminolevulinic acid[7] YesNoNoNoNoMethyl-5-aminolevulinic acidYesNoNoNoNoVerteporfin[8] YesNoNoNoNoPhotofrin[9] YesNoNoNoNoNeuroleptic drugs[10] Phenothiazines (chlorpromazine, fluphenazine, perazine, perphenazine, thioridazine)[11] YesYesYesNoNoThioxanthenes (chlorprothixene, thiothixene)YesNoNoNoNoAntifungalsTerbinafineNoNoNoNoYesItraconazoleYesYesNoNoNoVoriconazole[12, 13, 14, 15] YesNoNoYesNoGriseofulvinYesYesNoNoYesOther drugsPara-aminobenzoic acidYesYesNoNoNo5-FluorouracilYesYesYesYesNoPaclitaxel[2, 16] YesNoNoNoYesAmiodaroneYesNoNoYesNoDiltiazemYesNoNoNoYesQuinidineYesYesYesNoNoHydroxychloroquineNoNoYesNoNoCoal tarYesNoNoNoNoEnalaprilNoNoNoNoYesDapsoneNoYesYesYesNoOral contraceptives[17, 18] NoYesNoYesNoSunscreens[19] Para-aminobenzoic acidNoYesNoNoNoCinnamatesNoYesNoNoNoBenzophenonesNoYesNoNoNoSalicylatesNoYesNoNoNoFragrancesMusk ambretteNoYesNoNoNo6-MethylcoumarinNoYesNoNoNo*three-Hydroxy-three-methylglutaryl coenzyme A.
Phototoxic reactions occur as a result of the harmful effects of light-activated compounds on cell membranes and, in some instances, DNA. by contrast, photoallergic reactions are cell-mediated immune responses to a light-activated compound. Phototoxic reactions improve in most people if they are uncovered to sufficient quantities of sunshine and drug. normally, they appear as an exaggerated sunburn response, as proven within the picture under.
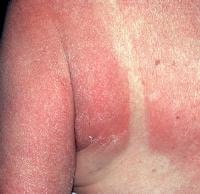 Phototoxic reaction.
Phototoxic reaction.Photoallergic reactions resemble allergic contact dermatitis, with a distribution restricted to sun-uncovered areas of the physique. on the other hand, when the reactions are severe or prolonged, they will extend into coated areas of pores and skin.
table 2. Distinguishing traits of Phototoxic and Photoallergic Reactions (Open table in a brand new window)
function Phototoxic response Photoallergic reaction IncidenceHighLowAmount of agent required for photosensitivityLargeSmallOnset of response after exposure to agent and lightMinutes to hours24-72 hoursMore than one exposure to agent requiredNoYesDistributionSun-uncovered skin onlySun-exposed skin, could unfold to unexposed areasClinical characteristicsExaggerated sunburnDermatitisImmunologically mediatedNoYes; type IV
Photoallergic reactions enhance in most effective a minority of individuals uncovered to the compound and lightweight; they're much less prevalent than phototoxic skin reactions. the amount of drug required to elicit photoallergic reactions is considerably smaller than that required for phototoxic reactions. moreover, photoallergic reactions, as proven in the picture beneath, are a form of cell-mediated immunity; their onset regularly is delayed by using as long as 24-72 hours after publicity to the drug and light. in contrast, phototoxic responses often happen within minutes or hours of sunshine exposure.
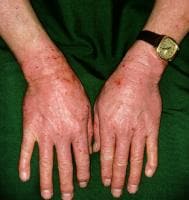 Photoallergic reaction. NextPathophysiologyPhototoxicity
Photoallergic reaction. NextPathophysiologyPhototoxicityPhototoxic reactions end result from direct injury to tissue because of a photoactivated compound. Many compounds have the potential to result in phototoxicity. Most have at the least one resonating double bond or an aromatic ring that can soak up radiant power. Most compounds are activated by way of wavelengths throughout the UV-A (320-400 nm) range, although some compounds have a peak absorption within the UV-B or seen vary.
In most instances, photoactivation of a compound results in the excitation of electrons from the secure singlet state to an excited triplet state. As excited-state electrons return to a extra stable configuration, they switch their energy to oxygen, resulting in the formation of reactive oxygen intermediates. Reactive oxygen intermediates corresponding to an oxygen singlet, superoxide anion, and hydrogen peroxide damage cell membranes and DNA. sign transduction pathways that lead to the production of proinflammatory cytokines and arachidonic acid metabolites are also activated. the end result is an inflammatory response that has the medical look of an exaggerated sunburn response.
The exception to this mechanism of drug-brought about phototoxicity is psoralen-brought on phototoxicity. Psoralens intercalate within DNA, forming monofunctional adducts. exposure to UV-A radiation produces bifunctional adducts within DNA. exactly how bifunctional adducts result in photosensitivity is unknown.
Photoallergic reactions
Photoallergic reactions are cell-mediated immune responses in which the antigen is a light-activated drug. Photoactivation results in the advance of a metabolite that can bind to protein carriers in the skin to kind a whole antigen. The response then proceeds exactly as other cell-mediated immune responses do. specifically, Langerhans cells and different antigen-providing cells absorb the antigen and then migrate to regional lymph nodes. In these locations, the Langerhans cells present the photoallergen to T lymphocytes that specific antigen-particular receptors. The T cells turn into activated and proliferate, and so they return to the web site of photoallergen deposition. in the pores and skin, the T cells orchestrate an inflammatory response that usually has an eczematous morphology if the photoallergen is applied topically or the characteristics of a drug eruption if the photoallergen is administered systemically.
PreviousNextEpidemiologyFrequencyUnited States
even though the incidence of drug-prompted photosensitivity in the U.S. is unsure. Phototoxic reactions are significantly more standard than photoallergic reactions.
international
The incidence of drug-precipitated photosensitivity is unknown.
Mortality/Morbidity
Drug-triggered photosensitivity is related to dying most effective in rare folks who are uncovered to large amounts of sunlight after taking massive doses of psoralens. even though mortality is rare, drug-caused photosensitivity can cause important morbidity in some folks, who should severely restrict their exposure to pure or synthetic mild. The carcinogenic doable as a result of extended publicity to those photosensitizing medication has been instructed; its clinical relevance continues to be to be determined.
Race
The racial incidence of drug-prompted photosensitivity reactions is unknown. Photosensitivity reactions can occur in races with closely pigmented pores and skin.
sex
men are more likely to have photoallergic reactions than girls.
Age
Drug-brought on photosensitivity reactions can occur in persons of any age.
PreviousProceed to medical Presentation , Drug-precipitated Photosensitivity

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.