the chance of great infection increases as the absolute neutrophil count (ANC) falls to the severely neutropenic range (
crucial update: Antifungal prophylaxis in neutropenic patients reduces possibility of invasive infections
In a systematic overview and diagnosis of findings from 25 randomized managed trials comprising greater than 70,000 patients, antifungal prophylaxis used to be effective in reducing the risk of invasive fungal infections in neutropenic patients receiving remedy for hematologic malignancies.[1, 2] Of the antifungals studied (fluconazole, itraconazole, micafungin, caspofungin, liposomal amphotericin B, voriconazole, posaconazole), more recent agents looked to be simpler than older dealers, with posaconazole one of the best. on the other hand, the investigators said antifungal prophylaxis had a much less mentioned impact in reducing all-lead to mortality (a secondary end result) in the neutropenic patients.[1, 2]
indicators and signs
fashionable offering symptoms of neutropenia embody the following:
Low-grade feverSore mouthOdynophagiaGingival pain and swellingSkin abscessesRecurrent sinusitis and otitisSymptoms of pneumonia (eg, cough, dyspnea)Perirectal ache and infection
patients with agranulocytosis frequently current with the following:
sudden onset of malaiseSudden onset of fever, presumably with chills and prostrationStomatitis and periodontitis accompanied through painPharyngitis, with issue swallowing
Lung infections are regularly bacterial or fungal pneumonias. bodily findings on examination of a affected person with neutropenia may just include the next:
FeverStomatitisPeriodontal infectionCervical lymphadenopathySkin an infection: The skin examination makes a speciality of rashes, ulcers, or abscessesSplenomegalyAssociated petechial bleedingPerirectal infectionGrowth retardation in kids
In agranulocytosis, the next may be current:
Fever (ceaselessly 40°C or larger)fast pulse and respirationHypotension and signs of septic shock if infection has been presentPainful aphthous ulcers within the oral cavitySwollen and gentle gums
See scientific Presentation for extra detail.
prognosis
earlier to an immense workup, rule out infectious and drug-caused reasons of neutropenia; then, receive the following laboratory research:
full blood rely: together with a manual differential in evaluating instances of agranulocytosisDifferential white blood cell countPeripheral smear assessment by way of a pathologist
the next research are applicable in some patients with neutropenia:
Antinuclear antibodyRheumatoid factorSerum immunoglobulin studies[3] Liver operate testsPeripheral blood go with the flow cytometryT-cell gene rearrangement for T-cell clonalityParoxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria trying out: by excessive-sensitivity or fluorescent aerolysin (FLAER)–primarily based go with the flow cytometryAntineutrophil antibodies: exams for antineutrophil antibodies must be carried out in sufferers with a historical past suggestive of autoimmune neutropenia and in these without a other evident explanation for agranulocytosis
Concurrent anemia, thrombocytopenia, and/or an bizarre outcome on a peripheral blood smear from a affected person with neutropenia recommend an underlying hematologic dysfunction. on this atmosphere, in an instant function a bone marrow aspiration and obtain a biopsy from the posterior iliac crest. Cytogenetic prognosis and cell-go with the flow diagnosis of the aspirate may be indicated.
See Workup for more element.
management
general measures to be taken in sufferers with neutropenia embody the following:
put off any offending drugs or retailers in circumstances involving drug exposure: If the identity of the causative agent is not known, stop administration of all drugs except the etiology is dependent Use careful oral hygiene to stop infections of the mucosa and teethAvoid rectal temperature measurements and rectal examinationsAdminister stool softeners for constipationUse excellent skin deal with wounds and abrasions: skin infections will have to be managed with the aid of someone with experience within the therapy of an infection in neutropenic sufferers
Antibiotics
begin specific antibiotic therapy to combat infections. This steadily entails the use of 1/3-technology cephalosporins or equivalents. Fever is also treated as an infection, as follows[4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] :
1/3-generation cephalosporins (eg, ceftazidime, cefepime) or imipenem-cilastatin and meropenem can be used as a single agentGentamicin or any other aminoglycoside should be brought if the neutropenic affected person’s condition is unstable or the person appears septic Beta-lactam antibiotics (eg, ticarcillin-clavulanate potassium, piperacillin-tazobactam) are usually utilized in combination with a third-technology cephalosporin or an aminoglycoside Vancomycin should be introduced if infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus or a Corynebacterium species is suspected
a brand new guiding principle from the American Society of scientific Oncology (ASCO) recommends that physicians try and forestall an infection in outpatients with "profound" neutropenia however no fever. It advises using antibacterial and antifungal prophylaxis if neutrophils are anticipated to remain under one hundred/µL for more than 7 days. the rule states that the ultimate agent for antibacterial prophylaxis is an oral fluoroquinolone, whereas that for antifungal prophylaxis is an oral triazole.[12, 13]
A precedence of the brand new ASCO tenet is to help clinicians identify sufferers with febrile neutropenia who don't want to be totally hospitalized. the rule subsequently calls for complication chance in patients with febrile neutropenia to be assessed with the Multinational affiliation for Supportive Care in cancer (MASCC) scoring device or with Talcott's rules.[12, 13]
Splenectomy
In people with neutropenia and Felty syndrome who've recurrent, existence-threatening bacterial infections, splenectomy is the remedy of possibility, although the response is frequently quick-lived. Systemic lupus related to autoimmune agranulocytosis may additionally respond to splenectomy or to immunosuppressive treatment.[14]
See treatment and drugs for extra element.
image library
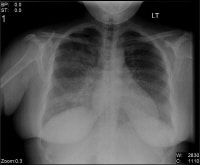 Bilateral interstitial infiltrates in a 31-12 months-old patient with influenza pneumonia. NextBackground
Bilateral interstitial infiltrates in a 31-12 months-old patient with influenza pneumonia. NextBackgroundNeutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophils in the nonmarginal pool, which constitutes four-5% of complete physique neutrophil stores.[15] many of the neutrophils are contained in the bone marrow, either as mitotically lively (one third) or postmitotic mature cells (two thirds).[16, 17, 7] Granulocytopenia is outlined as a diminished number of blood granulocytes, specifically neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. then again, the time period granulocytopenia is frequently used synonymously with neutropenia and, in that sense, is once more restrained to the neutrophil lineage by myself.
Neutropenia is defined when it comes to absolutely the neutrophil depend (ANC). The ANC is calculated by using multiplying the total white blood cell (WBC) rely via the share of neutrophils (segmented neutrophils or granulocytes) plus the band kinds of neutrophils in the whole blood depend (CBC) differential. See absolutely the Neutrophil depend calculator.
notice that many modern computerized contraptions in fact calculate and provide the ANC quantity of their reports. These units don't analyze one after the other bands from segmented neutrophils, and so the combined number is termed the absolute neutrophil count (ANC), representing each bands and more mature segmented neutrophils. If a band number is reported one at a time, usually by smear review, then you will divide the ANC into bands and segmented neutrophils by way of subtracting the absolute band number from the whole ANC.
The lower limit of the reference price for ANC in adults varies in different laboratories from 1.5-1.8 109/L or 1500-1800/µL (mm3). For sensible functions, a worth lower than 1500 cells/µL is in most cases used to outline neutropenia. Age, race, genetic background, atmosphere, and different elements can influence the neutrophil rely. for example, blacks will have a decrease however standard ANC value of a thousand cells/µL, with an ordinary whole WBC count.
Neutropenia is assessed as delicate, average, or extreme, based on the ANC. gentle neutropenia is existing when the ANC is a thousand-1500 cells/µL, average neutropenia is existing with an ANC of 500-one thousand/µL, and severe neutropenia refers to an ANC lower than 500 cells/µL. the chance of bacterial an infection is expounded to each the severity and duration of the neutropenia.
The time period agranulocytosis is used to be in contact a extra severe subset of neutropenia. Agranulocytosis refers to a virtual absence of neutrophils in peripheral blood. it's usually utilized to instances wherein the ANC is decrease than a hundred/μL.[17, 18, 19, 20] The reduced collection of neutrophils makes sufferers extremely prone to infection.[17, 21] Cardinal symptoms include fever, sepsis, and other manifestations of infection. reasons can embrace medicine, chemical compounds, infective agents, ionizing radiation, immune mechanisms, main bone marrow failure syndromes, and heritable genetic aberrations.
this text is restricted to discussing neutropenia (ANC aplastic anemia, pancytopenia, acute leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes).
For extra information, see the Medscape Reference article Pediatric Autoimmune and power Benign Neutropenia.
PreviousNextPathophysiology
Mature neutrophils are produced with the aid of precursors in the bone marrow. the total body neutrophil content material can also be divided conceptually into the next three booths: the bone marrow, the blood, and the tissues. within the marrow, the neutrophils exist in 2 divisions: the proliferative, or mitotic, compartment (myeloblasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes) and the maturation-storage compartment (metamyelocytes, bands, mature neutrophils, polymorphonuclear leukocytes ["polys"]).
Neutrophils go away the marrow storage compartment and enter the blood with out reentry into the marrow. within the blood, 2 booths are also current, the marginal compartment and the circulating compartment. Some neutrophils do not flow into freely (marginal compartment), however are adherent to the vascular surface, and these constitute approximately 1/2 of the entire neutrophils within the blood compartment.
Neutrophils leave the blood pool in a random method after 6-8 hours and enter the tissues, where they are destined for cell action or dying. as a consequence, if the method producing neutropenia is unknown, measurements of the blood neutrophil number, ANC, must steadily be supplemented by bone marrow examination to resolve whether adequate manufacturing of neutrophils or increased destruction of neutrophils exists.
web sites and mechanisms that result in neutropenia can be constrained to any of the three compartments or their subcomponents: bone marrow (mitotic or mature storage swimming pools); blood (circulating and marginal pools); or tissues (sequestration). for example, benign congenital neutropenias are related to a decrease in simplest the pool of circulating neutrophils however have fully normal marrow pools, marginal blood swimming pools, and tissue neutrophils.
Neutropenia can be resulting from insufficient or injured bone marrow stem cells, shifts in neutrophils from the circulating pool to the marginal blood or tissue pools, elevated destruction in the circulation, or combinations of those mechanisms. Intravascular stimulation of neutrophils through plasma-activated complement 5 (C5a) and endotoxin may result in increased margination alongside the vascular endothelium, decreasing the number of circulating neutrophils. Pseudoneutropenia refers to neutropenia as a result of such increased margination.[16, 22, 23, 24, 25]
disorders of the pluripotent myeloid stem cells and dedicated myeloid progenitor cells, which cause decreased neutrophil manufacturing, embrace some congenital types of neutropenia, aplastic anemia, acute leukemia, and myelodysplastic syndromes. different examples embody bone marrow tumor infiltration, radiation, an infection (particularly viral), and bone marrow fibrosis. cancer chemotherapy, different drugs, and toxins could harm hematopoietic precursors with the aid of directly affecting bone marrow.
The medical sequelae of neutropenia on a regular basis manifests as infections, most commonly of the mucous membranes. skin is the 2nd most common infection website, manifesting as ulcers, abscesses, rashes, and delays in wound healing. The genitalia and perirectum are also affected. on the other hand, the standard scientific indicators of an infection, together with native warmth and swelling, may be absent, as these require the presence of significant numbers of neutrophils. Fever, however, is often current, and its presence requires urgent consideration within the setting of severe neutropenia.
the risk of great an infection increases because the ANC falls to the severely neutropenic vary (
Bacterial organisms most frequently result in fever and infection in neutropenic patients. Fungal organisms are additionally vital pathogens in the atmosphere of neutropenia. traditionally, gram-terrible aerobic micro organism (eg, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Pseudomonas aeruginosa) had been most typical in these patients. on the other hand, gram-sure cocci, especially Staphylococcus species and Streptococcus viridans, have emerged as the most common pathogens in fever and sepsis as a result of the rising use of indwelling proper atrial catheters.
After treating neutropenic sufferers with vast-spectrum antibiotics for a couple of days, superinfection with fungi is popular. Candida species are the most continuously encountered organisms in this surroundings.
PreviousNextEtiology
The list for the entire potential causes of neutropenia isn't short. The etiology of neutropenia can conceptually be viewed in 2 huge methods, through mechanism or etiologic category.
The mechanisms that cause neutropenia are varied and now not utterly understood. in lots of cases, neutropenia occurs after extended drug or different exposure, resulting in decreased neutrophil manufacturing via hypoplastic bone marrow. this suggests an instantaneous stem cell toxic effect. In other circumstances, repeated however intermittent drug or other exposure is needed. this implies an immune mechanism, even though this concept has not been confirmed. in many scientific situations, the precise publicity and its length when it comes to the onset of neutropenia aren't known.
In view of our incomplete figuring out of the mechanisms for neutropenia, classification by means of huge etiologic category is simpler to hold. in this schema, the etiology of neutropenia can be labeled as either congenital (hereditary) or got. though this categorization may have limited medical diagnostic utility, it can be useful to clearly separate hereditary reasons of neutropenia from the panoply of got motives. within the atmosphere of hereditary neutropenias, these problems can be additional described as associated with remoted neutropenia or with different defects, whether or not immune or phenotypic.
Many hereditary disorders are as a result of mutations within the gene encoding neutrophil elastase, or ELA2. a number of alleles are involved. the most typical mutations are intronic substitutions that inactivate a splice website online in intron 4. Genes rather than ELA2 are also concerned. The desk below lists one of the vital genetic conditions concerned; these are exotic prerequisites.
table 1. Genetic (Hereditary) prerequisites in Agranulocytosis[26] (Open table in a brand new window)
SyndromeInheritanceGeneClinical FeaturesCyclic neutropeniaAutosomal dominantELA2Alternate 21-day biking of neutrophils and monocytesKostmann syndromeAutosomal recessiveUnknownStable neutropenia, no MDS or AMLSevere congenital neutropeniaAutosomal dominantELA2 (35-eighty four%)secure neutropenia, MDS or AMLAutosomal dominantGFI1Stable neutropenia, circulating myeloid progenitors, lymphopeniaSex linkedWaspNeutropenic variant of Wiskott-Aldrich syndromeAutosomal dominantG-CSFRG-CSF–refractory neutropenia, no AML or MDSHermansky-Pudlak syndrome type 2Autosomal recessiveAP3B1Severe congenital neutropenia, platelet dense-physique defect, oculocutaneous albinismChediak-Higashi syndromeAutosomal recessiveLYSTNeutropenia, oculocutaneous albinism, giant lysosomes, impaired platelet functionBarth syndromeSex linkedTAZNeutropenia, often cyclic; cardiomyopathy, methylglutaconic aciduriaCohen syndromeAutosomal recessiveCOH1Neutropenia, mental retardation, dysmorphismSource: Modified from Berliner et al, 2004.[26]
AML = acute myeloid leukemia; G-CSF = granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; MDS = myelodysplastic syndrome.
motives of got neutropenia are complex, but most are related to a few main categories: an infection, drugs (both direct toxic or immune mediated), and autoimmune. chronic benign neutropenia, or persistent idiopathic neutropenia, seems to be an overlap disorder with hereditary and bought forms, and is on occasion indistinguishable. Some neutropenic sufferers supply a transparent history and familial pattern, whereas others have no familial history, few blood check determinations, and an unknown period of neutropenia. This staff of patients will have hereditary or received neutropenia.[15, 27, 28, 29, 30] a brief summary of each congenital and acquired neutropenic disorders follows.
Congenital neutropenia with related immune defects
Neutropenia with abnormal immunoglobulins is seen in folks with X-linked agammaglobulinemia, remoted immunoglobulin A (IgA) deficiency, X-linked hyperimmunoglobulin M (XHIGM) syndrome, and dysgammaglobulinemia sort I.[31] In XHIGM, which is due to mutations within the CD40 ligand, sufferers can if truth be told have normal or accelerated levels of IgM but markedly diminished serum IgG levels. In all these disorders, the an infection chance is high, and the remedy is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).
patients with reticular dysgenesis exhibit severe neutropenia, no cell-mediated immunity, agammaglobulinemia, and lymphopenia.[31] life-threatening infections occur which might be refractory to granulocyte colony-stimulating issue (G-CSF).[32, 33, 34] Bone marrow transplantation is the therapy of option.
Congenital or continual neutropenias
severe congenital neutropenia (SCN), or Kostmann syndrome, is most regularly caused by a recessive inheritance and located in far flung, remoted populations with a high degree of consanguinity.[35] Autosomal dominant and sporadic circumstances have additionally been mentioned, most often because of mutations in the G-CSF receptor. No uniform genetic defect exists on this syndrome. Mutations in ELA2, which are causative for cyclic neutropenia (see beneath) usually are not enough to provide an explanation for the phenotype of Kostmann-like SCN.
patients existing by way of age 3 months with recurrent bacterial infections. The mouth and perirectum are the commonest sites of an infection. this kind of neutropenia is severe, and the therapy is G-CSF. risk of conversion to myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)/acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) with monosomy 7 after G-CSF therapies is associated with further got mutations. some of these cases are due to a mutation in the G-CSF receptor. patients whose situation responds clinically to G-CSF are treated for life.
Some sufferers with different types of SCN appear to have mutations in GFI1, a zinc-finger transcriptional repressor gene excited by hematopoietic stem cell function and lineage dedication selections.
Cyclic neutropenia (CN) is characterized by periodic bouts of neutropenia associated with infection, adopted by means of peripheral neutrophil depend restoration. Its periodicity is set 21 days (range, 12-35 d). Granulocyte precursors disappear from the marrow sooner than every neutrophil nadir within the cycle on account of accelerated apoptosis of myeloid progenitor cells.[22] Some cases could also be genetically determined with an autosomal recessive inheritance. other circumstances could also be as a result of an autosomal dominant inheritance. Some sporadic circumstances of CN have mutations in ELA2.
individuals with CN usually current as toddlers or children, however got kinds of CN in maturity exist. The prognosis is good with a benign route; on the other hand, 10% of sufferers will expertise lifestyles-threatening infections. The therapy for cyclic neutropenia is daily G-CSF.
power benign neutropenia
Affected individuals with persistent benign neutropenia have an total low possibility of infection.
Familial continual benign neutropenia is a dysfunction with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance observed in western Europeans, Africans, and Jewish Yemenites. patients are most often asymptomatic, and the infections are gentle. No specific therapy is required.
In nonfamilial power benign neutropenias, gentle infections with a benign course typify this disorder. The ANC, however, does reply to stress, such as infection, corticosteroids, and catecholamines.
Idiopathic power severe neutropenia
Idiopathic power severe neutropenia is a diagnosis of exclusion. Affected sufferers exhibit infections and severe neutropenia.
Neutropenia related to phenotypic abnormalities
Shwachman syndrome (Shwachman-Diamond) has an autosomal recessive inheritance sample. The neutropenia is moderate to extreme, with a mortality charge of 15-25%, and the syndrome gifts in infancy, with recurrent infections, diarrhea, and issue in feeding. Dwarfism, chondrodysplasia, and pancreatic exocrine insufficiency can happen.
Shwachman-Diamond syndrome and X-linked dyskeratosis congenita (DC), cartilage-hair hypoplasia (CHH), and Diamond-Blackfan anemia (DBA) all appear to share popular gene defects interested by ribosome synthesis. Most circumstances of Shwachman-Diamond syndrome are because of mutations in the SBDS gene.[36] the correct perform of this gene continues to be being elucidated; then again, it is fascinated about ribosome synthesis and RNA processing reactions. The treatment is G-CSF.
In CHH, the inheritance sample is autosomal recessive on chromosome 9, and it is noticed in Amish and Finnish families. CHH is because of mutations in the RMRP gene, which encodes the RNA component to the ribonuclease mitochondrial RNA processing (RNase MRP) complicated. The neutropenia is reasonable to extreme. CHH gifts with cell-mediated immunity defects, macrocytic anemia, gastrointestinal illness, and dwarfism. It additionally presentations a predisposition to most cancers, especially lymphoma. The treatment is bone marrow transplantation.
Dyskeratosis congenita (Zinsser-Cole-Engman syndrome) items with mental retardation, pancytopenia, and faulty cell-mediated immunity. Dyskeratosis congenita is extra in style in men than in women and is hematologically just like Fanconi anemia. Dyskeratosis congenita is usually X-linked recessive, even supposing autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive varieties of this disorder exist.
The X-linked recessive form of the dysfunction has been linked to mutations in DKC1, which encodes dyskerin, a nucleolar protein associated with ribonucleoprotein particles. The autosomal dominant type is related to mutations in any other gene, TERC, which is part of telomerase. Telomerase has each a protein and RNA element, and TERC codes the RNA element. sufferers with this disorder have shorter telomeres than customary. The remedy is G-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating issue (GM-CSF), and bone marrow transplantation.
Barth syndrome is an X-linked recessive disorder presenting with cardiomyopathy in infancy, skeletal myopathy, recurrent infections, dwarfism, and moderate to severe neutropenia.
Chediak-Higashi syndrome is an autosomal recessive dysfunction with recurrent infections, mental slowing, photophobia, nystagmus, oculocutaneous albinism, neuropathy, bleeding issues, gingivitis, and lysosomal granules in various cells. The neutropenia is average to severe, and the therapy is bone marrow transplantation.
Myelokathexis
Myelokathexis presents in infancy with reasonable neutropenia and is related to recurrent infections. The condition is as a result of accelerated apoptosis and diminished expression of bcl-x in neutrophil precursors. An odd nuclear appearance is seen, with hypersegmentation with nuclear strands, pyknosis, and cytoplasmic vacuolization. The treatment is G-CSF and GM-CSF.
Lazy leukocyte syndrome
Lazy leukocyte syndrome is a severe neutropenia with related bizarre neutrophil motility. The etiology is unknown, and the remedy is supportive in nature.
Metabolic issues
These are continual neutropenias with variable ANCs. They embody glycogen storage disease sort 1b and more than a few acidemias, reminiscent of isovaleric, propionic, and methylmalonic. In glycogen storage illness sort 1b, the therapy is G-CSF and GM-CSF.
obtained neutropenia as a result of intrinsic bone marrow illness
Intrinsic bone marrow ailments that may lead to neutropenia embody the following:
Aplastic anemiaHematologic malignancy (eg, leukemia, lymphoma, myelodysplasia, myeloma)Ionizing radiationTumor infiltrationGranulomatous infectionMyelofibrosisImmune-mediated neutropenia
A drug could act as a hapten and result in antibody formation. This mechanism operates in circumstances because of gold, aminopyrine, and antithyroid medicine. The antibodies spoil the granulocytes and would possibly not require the ongoing presence of the drug for his or her motion. instead, the drug may just type immune complexes that connect to the neutrophils. This mechanism operates with quinidine.
Drug immune-mediated neutropenia could also be because of the following:
AminopyrineQuinidineCephalosporinsPenicillinsSulfonamidesPhenothiazinesPhenylbutazoneHydralazineOther drugs have been implicated.
Autoimmune neutropenia is the neutrophil analogue of autoimmune hemolytic anemia and of idiopathic thrombocytopenic neutropenia. It will have to be considered in the absence of any of the standard causes. Antineutrophil antibodies were proven in these patients. Autoimmune neutropenia is also related to the following:
Crohn diseaseRheumatoid arthritis (with or with out Felty syndrome)Sjogren syndromeChronic, autoimmune hepatitisHodgkin lymphomaSystemic lupus erythematosusThymomaGoodpasture diseaseWegener granulomatosisPure purple blood cell (RBC) aplasia, in which there's complete disappearance of granulocyte tissue from the bone marrow; pure RBC dysplasia is a rare disorder as a result of the presence of antibody-mediated, granulocyte-macrophage colony forming unit (GM-CFU) inhibitory job, and it's frequently associated with thymomaTransfusion reactions, which may also be as a result of the skin antigens of neutrophilia; recipients of repeated granulocyte transfusions might turn into alloimmunized massive granular lymphocyte proliferation or leukemia
In isoimmune neonatal neutropenia, the mum produces IgG antineutrophil antibodies to fetal neutrophil antigens which might be recognized as nonself. this occurs in three% of live births. The dysfunction manifests as neonatal fever, urinary tract infection, cellulitis, pneumonia, and sepsis. The length of the neutropenia is in most cases 7 weeks.
continual autoimmune neutropenia is observed in adults and has no age predilection. As many as 36% of sufferers will exhibit serum antineutrophil antibodies, and the scientific route is frequently less extreme. sufferers can have this disorder in affiliation with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Wegener granulomatosis, and chronic hepatitis.
If continual autoimmune neutropenia is related to these ailments, corticosteroids are indicated as remedy. In neonates and children, this disorder is related to a decrease chance of infection and milder infections involving the center ear, gastrointestinal tract, and skin.
T-gamma lymphocytosis, or lymphoproliferative dysfunction, is a clonal disease of CD3+ T lymphocytes or CD3- pure killer (NK) cells that infiltrate the bone marrow and tissues. sometimes called leukemia of huge granular lymphocytes (LGL-leukemia), T-gamma lymphocytosis can also be associated with rheumatoid arthritis and is related to high-titer antineutrophil antibodies. The neutropenia is continual and extreme. The therapy is steadily supportive in nature, however it is usually directed at taking out the clonal inhabitants.
got neutropenia resulting from infection
Infections are the most common type of bought neutropenia. Infections that can lead to neutropenia include, however aren't limited to, the next:
Bacterial sepsisViral infections (eg, influenza, measles, Epstein Barr virus [EBV], cytomegalovirus [CMV], viral hepatitis, human immunodeficiency virus [HIV]-1) (see first image beneath)ToxoplasmosisBrucellosisTyphoidTuberculosis (see 2d and third images beneath)MalariaDengue feverRickettsial infectionBabesiosis
 Bilateral interstitial infiltrates in a 31-12 months-old patient with influenza pneumonia.
Bilateral interstitial infiltrates in a 31-12 months-old patient with influenza pneumonia. 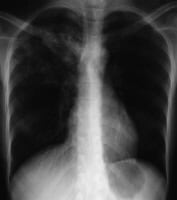 Anteroposterior chest radiograph in a younger ED affected person imparting with cough and malaise. The radiograph presentations a traditional posterior phase right higher lobe density consistent with active tuberculosis. This girl used to be admitted to isolation and started empirically on a 4-drug regimen in the ED. Tuberculosis was once demonstrated on sputum checking out. image courtesy of remote drugs, remotemedicine.org.
Anteroposterior chest radiograph in a younger ED affected person imparting with cough and malaise. The radiograph presentations a traditional posterior phase right higher lobe density consistent with active tuberculosis. This girl used to be admitted to isolation and started empirically on a 4-drug regimen in the ED. Tuberculosis was once demonstrated on sputum checking out. image courtesy of remote drugs, remotemedicine.org. 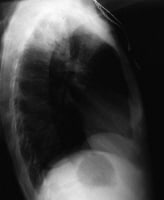 Lateral chest radiograph in a 31-year-outdated affected person with influenza pneumonia. picture courtesy of far off drugs, remotemedicine.org.
Lateral chest radiograph in a 31-year-outdated affected person with influenza pneumonia. picture courtesy of far off drugs, remotemedicine.org.essentially the most repeatedly involved organisms are from endogenous flowers. Staphylococcus aureus organisms are present in instances of skin infections. Gram-bad organisms are seen in infections of the urinary and gastrointestinal tracts, specifically Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas species. Candida albicans infections may additionally occur. blended flora may be discovered in the oral cavity.
Viral infections frequently result in mild or reasonable neutropenia. Agranulocytosis is rare but may occur. the most typical organisms are Epstein-Barr virus, hepatitis B virus, yellow fever virus, cytomegalovirus, and influenza. Many overwhelming infections, both viral and bacterial, could lead to extreme neutropenia.
got neutropenia resulting from dietary deficiency
dietary deficiencies that can result in neutropenia embody vitamin B-12, folate, and copper deficiency.
bought neutropenia as a result of drugs and chemical compounds, except for cytotoxic chemotherapy
a large number of medicine had been associated with neutropenia. The very best chance categories are antithyroid medicines, macrolides, and procainamides. As said above, many medication act with the aid of an immune-mediated mechanism. on the other hand, some drugs appear to have direct poisonous effects on marrow stem cells or neutrophil precursors in the mitotic compartment. for instance, medication such as the antipsychotics and antidepressants and chloramphenicol may act as direct toxins in some individuals, according to metabolism and sensitivity on this method. different medication will have a combination of immune and nonimmune mechanisms or will have unknown mechanisms of motion.
Antimicrobials include penicillin, cephalosporins, vancomycin, chloramphenicol, gentamicin, clindamycin, doxycycline, flucytosine, nitrofurantoin, novobiocin, minocycline, griseofulvin, lincomycin, metronidazole, rifampin, isoniazid, streptomycin, thiacetazone, mebendazole, pyrimethamine, levamisole, ristocetin, sulfonamides, chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, quinacrine, ethambutol, dapsone, ciprofloxacin, trimethoprim, imipenem/cilastatin, zidovudine, fludarabine, acyclovir, and terbinafine.[37]
Analgesics and anti-inflammatory agents embrace aminopyrine, dipyrone, phenylbutazone, indomethacin, ibuprofen, acetylsalicylic acid, diflunisal, sulindac, tolmetin, benoxaprofen, barbiturates, mesalazine, and quinine.
Antipsychotics, antidepressants, and neuropharmacologic retailers embrace phenothiazines (chlorpromazine, methylpromazine, mepazine, promazine, thioridazine, prochlorperazine, trifluoperazine, trimeprazine), clozapine, risperidone, imipramine, desipramine, diazepam, chlordiazepoxide, amoxapine, meprobamate, thiothixene, and haloperidol.
Anticonvulsants embrace valproic acid, phenytoin, trimethadione, mephenytoin (Mesantoin), ethosuximide, and carbamazepine.
Antithyroid medication include thiouracil, propylthiouracil, methimazole, carbimazole, potassium perchlorate, and thiocyanate.
Cardiovascular medication embrace procainamide, captopril, aprindine, propranolol, hydralazine, methyldopa, quinidine, diazoxide, nifedipine, propafenone, ticlopidine, and vesnarinone.
Antihistamines embrace cimetidine, ranitidine, tripelennamine (Pyribenzamine), methaphenilene, thenalidine, brompheniramine, and mianserin.
Diuretics embody acetazolamide, bumetanide, chlorothiazide, hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, methazolamide, and spironolactone.
Hypoglycemic marketers embody chlorpropamide and tolbutamide.
Antimalarial medicine include amodiaquine, dapsone, hydroxychloroquine, pyrimethamine, and quinine.
Miscellaneous medicine embrace allopurinol, colchicine, aminoglutethimide, famotidine, bezafibrate, flutamide, tamoxifen, penicillamine, retinoic acid, metoclopramide, phenindione, dinitrophenol, ethacrynic acid, dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), cinchophen, antimony, pyrithyldione, rauwolfia, ethanol, chlorpropamide, tolbutamide, thiazides, spironolactone, methazolamide, acetazolamide, IVIG, and levodopa.
Heavy metals embrace gold, arsenic, and mercury.
publicity to medication or chemical substances is the commonest cause of agranulocytosis: about one half of of patients have a historical past of medication or chemical exposure. Any chemical or drug that may depress the bone marrow and result in hypoplasia or aplasia is capable of inflicting agranulocytosis. Some drugs do this to everyone if they are administered in sufficiently big doses. other dealers appear to lead to idiosyncratic reactions that affect best sure susceptible folks.
Some dealers (eg, valproic acid, carbamazepine, and beta-lactam antibiotics) act by means of direct inhibition of myelopoiesis. In bone marrow cultures, these agents inhibit granulocyte colony formation in a dose-associated model. Direct injury to the bone-marrow microenvironment or myeloid precursors plays a role in most other instances.
Many medication related to agranulocytosis were mentioned to the united states meals and Drug Administration (FDA) below its adversarial reactions reporting requirement. Many agents are additionally stated to a registry maintained by the American clinical association (AMA). The said medication have been used by myself, together with some other drug recognized to be doubtlessly poisonous, or with any other drug with out known toxicity. several medicine are particularly salient on account of their high frequency of association with agranulocytosis. They include the following:
PhenothiazineAntithyroid medicine (thiouracil and propylthiouracil)AminopyrinePhenylbutazoneChloramphenicolSulfonamidesMiscellaneous immunologic neutropenias
Immunologic neutropenias may just occur after bone marrow transplantation and blood product transfusions.
Felty syndrome is a syndrome of rheumatoid arthritis, splenomegaly, and neutropenia. Splenectomy presentations an preliminary response, but neutropenia may recur in 10-20% of patients. remedy is directed toward rheumatoid arthritis.
In complement activation–mediated neutropenia, hemodialysis, cardiopulmonary bypass, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) expose blood to artificial membranes and can result in complement activation with subsequent neutropenia.
In splenic sequestration, the degree of neutropenia attributable to this process is proportional to the severity of the splenomegaly and the bone marrow’s ability to catch up on the discount in circulating bands and neutrophils.
Eosinopenia and basophilopenia
Eosinopenia could also be associated with the following:
Acute bacterial infectionGlucocorticoid administrationHypogammaglobulinemiaPhysical stressThymoma
lowered circulating basophils is also related to the next:
AnaphylaxisAcute infectionDrug-induced hypersensitivityCongenital absence of basophilsHemorrhageHyperthyroidismIonizing radiationNeoplasiaOvulationUrticariaDrugs (eg, corticosteroid, adrenocorticotropic hormone [ACTH] remedy, chemotherapeutic retailers, thyroid hormones)
Go to Pediatric Autoimmune and persistent Benign Neutropenia for full knowledge on this subject.
PreviousNextEpidemiology
The incidence of drug-brought on neutropenia is 1 case per million individuals per yr. the precise frequency of agranulocytosis is unknown; the estimated frequency is 1.zero-3.4 cases per million population per yr.
Age distribution for neutropenia
Age can influence the neutrophil depend. aged people have a better incidence rate of neutropenia than youthful folks.
Agranulocytosis occurs in all age teams. The congenital varieties are most common in childhood; got agranulocytosis is commonest in the aged population.[29] Go to Pediatric Autoimmune and power Benign Neutropenia for complete data on this matter.
sex distribution for neutropenia
Neutropenia happens extra repeatedly in girls than in men. Agranulocytosis happens fairly more ceaselessly in ladies than in males, possibly as a result of their increased charge of medicine usage. whether or not this greater frequency is related to the increased incidence of autoimmune illness in ladies is unknown.
Incidence of neutropenia by race or ethnicity
Race and genetic historical past can affect ANC. Blacks, Ethiopians, Yemenite Jews, and sure populations on this planet could have decrease ANCs as a result of decrease WBC counts. information from US national well being and dietary examination 1999 to 2004 survey found the prevalence of neutropenia to be 4.5% amongst black individuals, 0.seventy nine% in white folks, and nil.38% in Mexican-american citizens.[38] Blacks have a decrease neutrophil count both due to faulty granulocyte release from normal bone marrow, or they will have a compromised bone marrow reserve.
The incidence fee of neutropenia was once studied in NY city in 2008 in 261 wholesome girls aged 20-70 years of various ethnicity.[39] The incidence charge was 10.5% among US blacks. American and European white people and those from the Dominican Republic had a 0% incidence fee. other ethnic groups integrated those from Haiti, 8.2% incidence price; Barbados/Trinidad-Tobago, 6.4%; and Jamaica, 2.7%.[39]
Agranulocytosis has no racial predilection.
PreviousNextPrognosis
The prognosis of a patient with neutropenia depends on the principle etiology, duration, and severity of the neutropenia. better wide-spectrum antibiotic retailers, mixed with enhanced supportive care, have improved the prognosis for many patients with extreme neutropenia. in a roundabout way, affected person survival is dependent upon the recovery of adequate neutrophil numbers.
Morbidity in these with neutropenia usually includes infections right through extreme, extended episodes of neutropenia. The infections may be superficial, involving primarily the oral mucosa, gums, skin, and sinuses, or they is also systemic, with existence-threatening septicemia.
severe scientific issues happen in 21% of patients with most cancers and neutropenic fever. Mortality correlates with the length and severity of the neutropenia and the time elapsed until the primary dose of antibiotics is administered for neutropenic fever.[34, 40, 41] Neutropenic fever in most cancers sufferers contains an total mortality fee of four-30%.
the three recognized excessive-possibility groups among cancer patients with neutropenic fever (lots of whom have acquired aggressive chemotherapy) are inpatients with fever while developing neutropenia, outpatients requiring acute sanatorium take care of problems past neutropenia and fever, and stable outpatients with uncontrolled most cancers.
If agranulocytosis is untreated, the risk of loss of life is high. demise results from uncontrolled sepsis. If the situation may also be reversed with therapy, the danger of demise is low. Antibiotic and antifungal medicines can cure the an infection if the ANC rises. Agranulocytosis secondary to viral infections is frequently self-restricted, and patients with such prerequisites have a good prognosis.
Drug-brought about agranulocytosis carries a mortality fee of 6-10%. If treated at once and vigorously, patients with drug-induced agranulocytosis have a excellent prognosis.
PreviousNextPatient education
sufferers with neutropenia will have to be urged to avoid exposure to folks with respiratory tract infections.[42] They will have to steer clear of overcrowded areas, and if their ANC is lower than a thousand/µL, they must put on a facemask in public locations.
sufferers should be recommended to keep away from any drug that was up to now implicated in causing them neutropenia. They will have to be educated about the importance of universal CBC checking out within the preliminary length when a new drug with a high propensity to lead to neutropenia is presented. the exact frequency of testing will depend on the precise drug and the time route of neutropenia association. at the first sign of a drop in the ANC, the drug should be discontinued.
in the office, folks should be trained to follow laws from the Occupational security and well being Administration (OSHA) that cover security precautions when they care for poisonous substances.
For affected person education knowledge, see the Blood and Lymphatic device heart and Immune system heart, in addition to Anemia, Sepsis (Blood an infection), Leukemia, and Lymphoma.
PreviousProceed to medical Presentation , Neutropenia

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.