within the late 19th century, serum used to be found to include a nonspecific warmth-labile complementary concept that interacted with antibodies to set off bacteriolysis. Ehrlich and Morgan termed this factor complement.
The complement system as understood nowadays is a multimolecular machine composed of more than 32 proteins and consisting of serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors that bind to enrich fragments. They represent 10% of the globulin fraction of serum. Many of these proteins are unique by way of the letter C (C1, four, 2, three, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) and are assigned numbers within the order of their discovery. See tables 1-6 in Pathophysiology for extra information.
NextPathophysiology
The complement gadget consists of 7 serum and 9 membrane regulatory proteins, 1 serosal regulatory protein, and 8 cell membrane receptors that bind complement fragments. Most are synthesized primarily via the liver. Exceptions are C1, factor D, and properdin. These are almost certainly synthesized through macrophages and even via T lymphocytes.
The tables on this section have been adapted from Middleton's Textbook of hypersensitive reaction and Immunology, sixth edition; information are notably from Morley BJ, Walport MJ, eds: The complement details guide, San Diego, 2000. Acute-segment ranges are estimates in keeping with restricted information.
PreviousNextActivation
The complement machine functions as an interactive sequence, with one reaction resulting in another in the form of a cascade. it is initiated by all kinds of substances and has 2 phases. in the first phase, a series of explicit interactions leads to formation of intrinsic complement proteinase, termed C3 convertase. depending on the character of complement activators, the basic pathway, the choice pathway, or the more lately found out lectin pathway is activated predominantly to provide C3 convertase. every of those pathways makes use of totally different proteins. The 2d segment for each involves cleavage of C3b, producing multiple biologically essential fragments and large, potentially cytolytic complexes. See the image below.
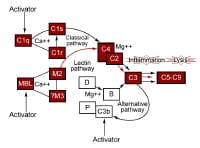 Activation of the complement pathways. traditional pathway
Activation of the complement pathways. traditional pathwayThis pathway has 2 units. One, the recognition unit, contains a trimolecular advanced of C1q, 2 molecules of C1r, and a couple of molecules of C1s held together with the aid of calcium. the opposite is an activation unit of C2, C3, and C4. The sequence begins with the binding of 2 or extra C1q reputation gadgets to the Fc nonantigen binding a part of IgG and IgM molecules. This induces a conformational trade, resulting in autoactivation of C1r that then cleaves C1s to its active state. This then acts similarly to C1 esterase and cleaves C2 and C4 to kind C2aC4b, which is the C3 esterase that cleaves C3 to kind C3b. C1q can also be activated through mycoplasmal organisms, RNA viruses, bacterial endotoxins, and cell membranes of some organelles with out the presence of antibody.
table 1. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) machine, Classical Pathway* (Open table in a brand new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)commonplace Serum ranges (µg/mL)Acute phase Serum levels (% increase)Chromosomal LocationC1q4607013%1p34-36.3C1r833412p13C1s833147p.c12p13C420060034p.c6p21.3C2102236p21.three*C-reactive protein (CRP, now not shown) leads to basic pathway activation analogous to lectin pathway activation by MBL and ficolins. Alternate pathway
This was found out with the aid of Pillemer and colleagues in 1954 however used to be identified universally some years later. This pathway is activated by viruses, fungi, bacteria, parasites, cobra venom, immunoglobulin A, and polysaccharides and varieties a very powerful a part of the safety mechanism impartial of the immune response. here, C3b binds to factor B that's cleaved via issue D to Bb. C3bBb complicated then acts as the C3 convertase and generates extra C3b thru an amplification loop. Binding of issue H to C3b will increase its inactivation by using factor I. Properdin stabilizes it, fighting its inactivation via components H and i. The alternate pathway does now not lead to a very nonspecific activation of complement because it requires particular kinds of compounds for activation. It merely does no longer require specific antigen-antibody interactions for initiation.
table 2. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) machine, various Pathway (Open desk in a new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)commonplace Serum levels (µg/mL)Acute phase Serum ranges (% increase)Chromosomal LocationFactor D25219Factor B939365p.c6p21.1-21.3Lectin pathway
The lectin or mannan-binding pathway is activated similar to the classic pathway with the exception of that lectin replaces the antibody and mannan-binding lectin–associated proteases change C1 enzymatic job. instead, mannan-binding lectin binds to sugar residues on the skin of a pathogen. Mannan-binding lectin is related to serine proteases, just like the C1r and C1s subcomponents of the basic pathway, that also activate C4 and C2, forming the classical pathway C3 convertase C4b2a.
desk three. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) gadget, Lectin Pathway (Open table in a brand new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)commonplace Serum levels (µg/mL)Acute segment Serum ranges (% elevate)Chromosomal LocationMBL288-5762Up to 1000%10q11.2-21.0MASP-1976...3q27-28MASP-280......1p36.23-36.31MASP-3105......3q27-28Map1919......1p36.23-36.31L-ficolin/P3563013.7...9H-ficolin/Hakata antigen63015......MBL = mannan-binding lectin; MASP = MBL-related serine proteaseMembrane attack complicated
only 5 proteins are involved within the direct killing of cells. C2a4b3b complicated from the basic or MBL pathways or C3bBb from the choice pathway cleaves C5. C5b prompts the terminal complement pathway via associating with C6, C7, and C8 to kind macromolecular complexes denoted as C5b-eight, which is able to bind to cell membranes. C9 binds to this complex, inducing a conformational exchange that exposes a brand new antigenic website online referred to as C9 neoantigen. further C9 molecules bind to membrane-certain C5b-9, forming ringlike pores, resulting in transmembrane channels that cause cell lysis.
table 4. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) device, C3 and Terminal parts (Open desk in a brand new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)commonplace Serum ranges (µg/mL)Acute section Serum levels (% increase)Chromosomal LocationC3185120030p.c19p13.2-13.3C51907555percent9q33C6128455p12-14C7120555p12-14C8163681p32; 9q34.3C9796049p.c5p13PreviousNextRegulation
The complement device serves a very important role in host defense, but whether it is directed in opposition to self, it could actually result in critical illness. subsequently, it's carefully regulated at nearly every step. See the image under.
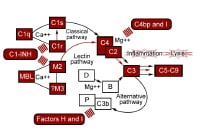 keep an eye on proteins of the complement pathways. basic pathway
keep an eye on proteins of the complement pathways. basic pathwayThe basic pathway requires the identification of a goal by using the presence of an antibody. C1 inhibitor (C1-INH) inhibits C1r and C1s by using binding covalently to them, causing disassembly of C1 macromolecular complicated. The inhibitor is synthesized in the liver and blood monocytes; its gene is situated on chromosome 11. C2a4b could be very labile and undergoes spontaneous decay with unencumber of C2a and lack of enzymatic job. C4 binding protein binds C4, which hurries up its price of dissociation from C2a and makes C4b extra at risk of proteolysis with the aid of issue I. Membrane-sure decay-accelerating issue (DAF) promotes unlock of C2a from C4b2a via physically interfering with C4b and C2a affiliation.
table 5. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) machine, keep watch over Proteins in Serum (Open table in a brand new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)customary Serum levels (µg/mL)Acute phase Serum levels (% raise)Chromosomal LocationC1 inhibitor10515021%11q11-13.1C4-binding protein550225...1q3.2Factor H150550...1q3.2Factor I8835...4q25Properdin2235-14%Xp11.23-11.30S protein75340...17q11Clusterin80340...8p21Anaphylotoxin inactivator29035...8p22-23, 10Alternative pathway
Carbohydrate composition and its sialic acid content material on the cell floor play the most important role in the activation of the alternate pathway. Sialic acid blocks activation by favoring the binding of factor H to C3b, which is then inactivated by factor I.[1] Microorganisms missing sialic acid are killed, whereas human cells covered with glycophorin A, a sialoglycoprotein, are protected.
C3bBb is moderately labile and undergoes spontaneous decay thru dissociation of Bb. Properdin is synthesized with the aid of monocytes and T lymphocytes. Properdin binds to C3bBb and stabilizes it, fighting its decay. issue H competes with factor B for binding to C3b and displaces Bb from C3bBb. It hurries up the inactivation of C3b by using factor I. issue I inactivates C3b to iC3b, a molecule that can't perform enzymatically. Complement receptor 1 (CR1) has issue H–like task, permitting factor I to cleave C3b. Membrane cofactor protein additionally has issue H–like task, primarily for alternative C3 convertase.
Membrane assault advanced
Homologous restriction factor, C8 binding protein, is a cell membrane protein with significant sequence homology to both C8 and C9 and is broadly dispensed on peripheral blood cells. It prevents the interaction of C8 and C9. Membrane-bound CD59, sometimes called homologous restriction issue 20, prevents the binding of C5b-8 to C9 and inhibits the unfolding of C9 that's required for polymerization and formation of macroscopic pores in the cell membrane. S protein (vitronectin) binds to C5b-7 and abolishes its task. SP-forty,forty (clusterin) has results similar to vitronectin.
desk 6. Proteins of the Human Complement (C) device, Membrane Receptor and keep an eye on Proteins (Open desk in a new window)
ComponentMol Wt (~kD)LigandsChromosomal LocationDAF70C4b2a1q3.2MCFP60C3b1q3.2CD5920C8, C911p13-14CR1250C3b, C4b1q3.2CR2145C3dg, C3d, EBV1q3.2CR3250iC3b, LPS, β-glucans16p11-13.1, 21q22.3CR4245iC3b, LPS16p11.2, 21q22.3C3aR100C3a, C4a12p13C5aR50C5a19q13.three-13.4DAF = decay-accelerating issue; MCFP = membrane cofactor protein; EBV = Epstein-Barr virus; LPS = lipopolysaccharidesPreviousNextBiologic effects
The biologic effects of complement embrace promoting of chemotaxis and anaphylaxis, opsonization and phagocytosis of microorganisms, and removing of immune complexes from the circulation. Most complement elements are acute phase reactants, and their focus will increase in states of infection, trauma, and harm.
C3a and C5a are anaphylatoxins and bind to mast cells, triggering the discharge of histamine and other mediators, resulting in vasodilation, erythema, and swelling. When C3a or C5a is injected into the pores and skin, it elicits an instantaneous wheal and flare response, just like that discovered with allergen injection into the skin of individuals with hypersensitive reactions. C3a and C5a additionally produce bronchoconstriction with human tracheal or bronchial muscle strips in vitro. C5a is an enormous stimulus for inflow of neutrophils, basophils, monocytes, and eosinophils.
C3b fixes to the antigen-antibody complicated and enables its adherence to cells (eg, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes) that have receptors for C3b. This explicit action of opsonization helps in phagocytosis. C3b-lined particles also bind to B lymphocytes and spark off them to beef up the primary antibody response. Immune complexes shaped within the circulation are lined with C3b and bind to erythrocytes, which then transport them to the liver and spleen for elimination. This course of maintains the solubility of the immune complexes. in the early phases of viral an infection, when the amount of antibody is limited, the fixation of C3b to the viral antigen-antibody advanced increases neutralization.
The terminal components of the complement machine result in lysis of virus-contaminated cells, tumor cells, and a few gram-bad microorganisms. They actually have a function in neutralization of endotoxins in vitro and protection from their deadly results in experimental animal fashions. C5b-9 neoantigen is found within the muscle in dermatomyositis, implying that the terminal complement machine can have a task within the pathophysiology of that disease.
PreviousProceed to clinical Presentation , Complement-related problems

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.